In addition to international standards, most countries have their own national safety standards and regulations for electric heating devices. These standards are often based on international standards but may include additional requirements to address local conditions and needs.
In the United States, the Underwriters Laboratories (UL) is a private organization that develops safety standards for electrical products, including electric heating devices. UL standards are widely recognized and used by manufacturers, retailers, and regulatory bodies. UL 1278, for example, is a standard for electric space heaters, which specifies safety requirements for construction, performance, and testing.
The European Union has its own set of safety standards and regulations for electric heating devices, known as the CE marking. The CE marking indicates that a product meets the essential safety requirements of the European Union's directives, including the Low Voltage Directive and the Machinery Directive. To obtain the CE marking, manufacturers must ensure that their products comply with relevant European standards, such as for electric space heaters.
In Canada, the Canadian Standards Association (CSA) develops safety standards for electrical products. CSA standards are similar to UL standards and are used to ensure the safety of electric heating devices in Canada.
Key Safety Requirements
The safety standards and regulations for electric heating devices cover a wide range of requirements, including the following:
1. Protection Against Electric Shock
Electric heating devices must be designed to protect users against electric shock. This includes using insulation materials to prevent contact with live parts, ensuring that electrical connections are secure, and providing protection against short circuits and overloads. Grounding is also an important safety feature, as it provides a path for electrical current to flow to the ground in the event of a fault, preventing electric shock.
2. Protection Against Fire
Fire is a major hazard associated with electric heating devices, so safety standards and regulations include requirements to prevent fires. This includes using fire-resistant materials for the housing and heating elements, ensuring that the device does not overheat, and providing thermal cut-off devices that automatically shut off the device if it becomes too hot. Electric heating devices must also be designed to prevent the accumulation of dust and debris, which can ignite and cause a fire.
3. Mechanical Safety
Electric heating devices must be designed to be mechanically safe, with no sharp edges or moving parts that could cause injury. The device must also be stable and not tip over easily, as a tipped-over heater can come into contact with flammable materials and cause a fire.
4. Testing and Certification
To ensure that electric heating devices meet safety standards, they must undergo rigorous testing by accredited testing laboratories. Testing includes checks for electric shock protection, fire safety, mechanical safety, and performance. Once a device has passed all tests, it is awarded a certification mark, such as UL, CE, or CSA, which indicates that it meets the relevant safety standards.
5. Labeling and Instructions
Electric heating devices must be labeled with important safety information, such as the voltage rating, power consumption, and certification marks. They must also come with detailed instructions for use, installation, and maintenance, including warnings about potential hazards and how to avoid them.
Enforcement of Safety Standards and Regulations
The enforcement of safety standards and regulations for electric heating devices is the responsibility of government agencies and regulatory bodies. In many countries, these agencies conduct inspections of manufacturers, retailers, and importers to ensure that electric heating devices comply with safety standards. They may also issue recalls of products that are found to be unsafe.
Consumers also play a role in ensuring the safety of electric heating devices. By purchasing products that have been certified by recognized organizations, such as UL, CE, or CSA, consumers can reduce the risk of using unsafe devices. It is also important for consumers to read and follow the instructions for use, installation, and maintenance, and to inspect their electric heating devices regularly for signs of damage or wear.
Conclusion
Safety standards and regulations are essential for ensuring the safe use of electric heating devices. They provide a framework for manufacturers to design, produce, and test their products to meet minimum safety requirements, protecting consumers and workers from fire, electric shock, and other hazards. International and national standards, such as those developed by the IEC, UL, and CSA, ensure that electric heating devices are safe and reliable, regardless of where they are manufactured or sold.
As technology continues to advance, safety standards and regulations will need to evolve to address new risks and challenges. Manufacturers, regulatory bodies, and consumers must work together to ensure that electric heating devices remain safe and efficient, providing warmth and comfort without compromising on safety.
 Cartridge Heaters Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge Heaters Cartridge Heaters Cartridge Heaters Cartridge Heaters
Cartridge Heaters Cartridge Heaters Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters
Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters
Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters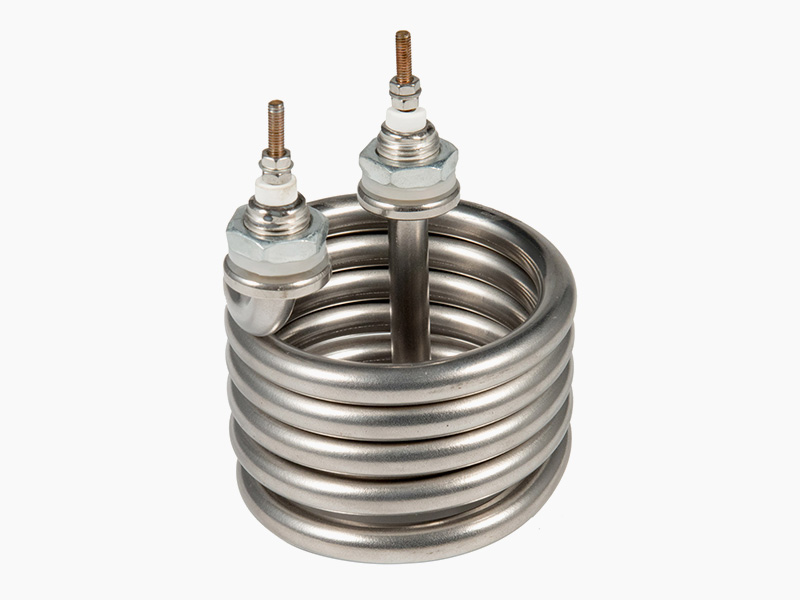 Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters
Tubular Heaters Tubular Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters
Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters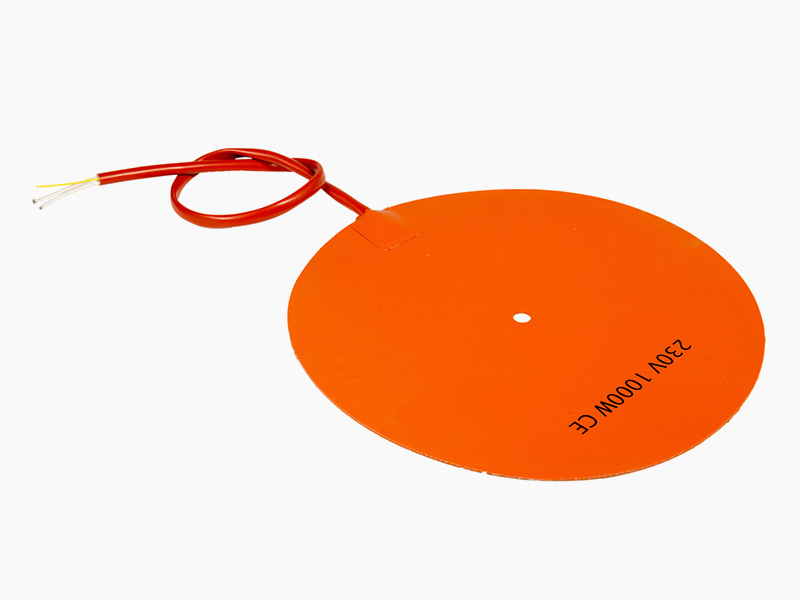 Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters
Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters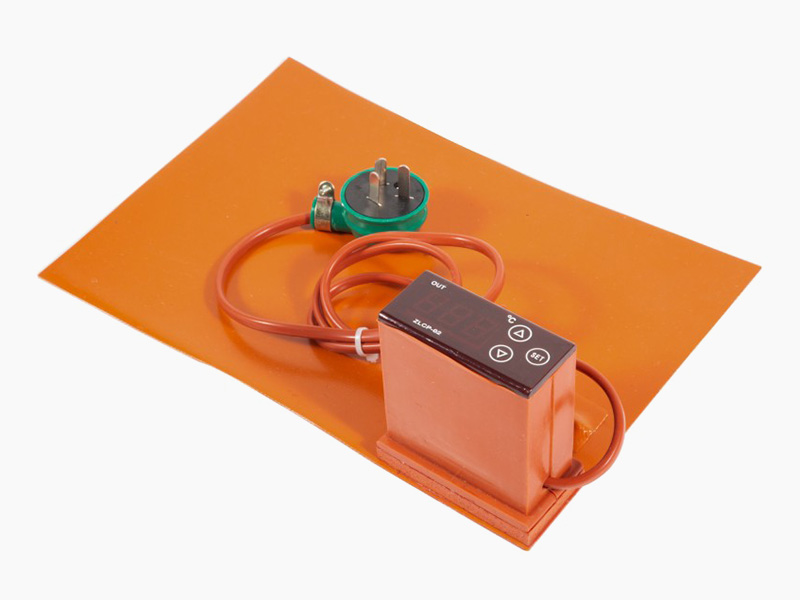 Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters
Silicone Rubber Heaters Silicone Rubber Heaters

 русск
русск Español
Español